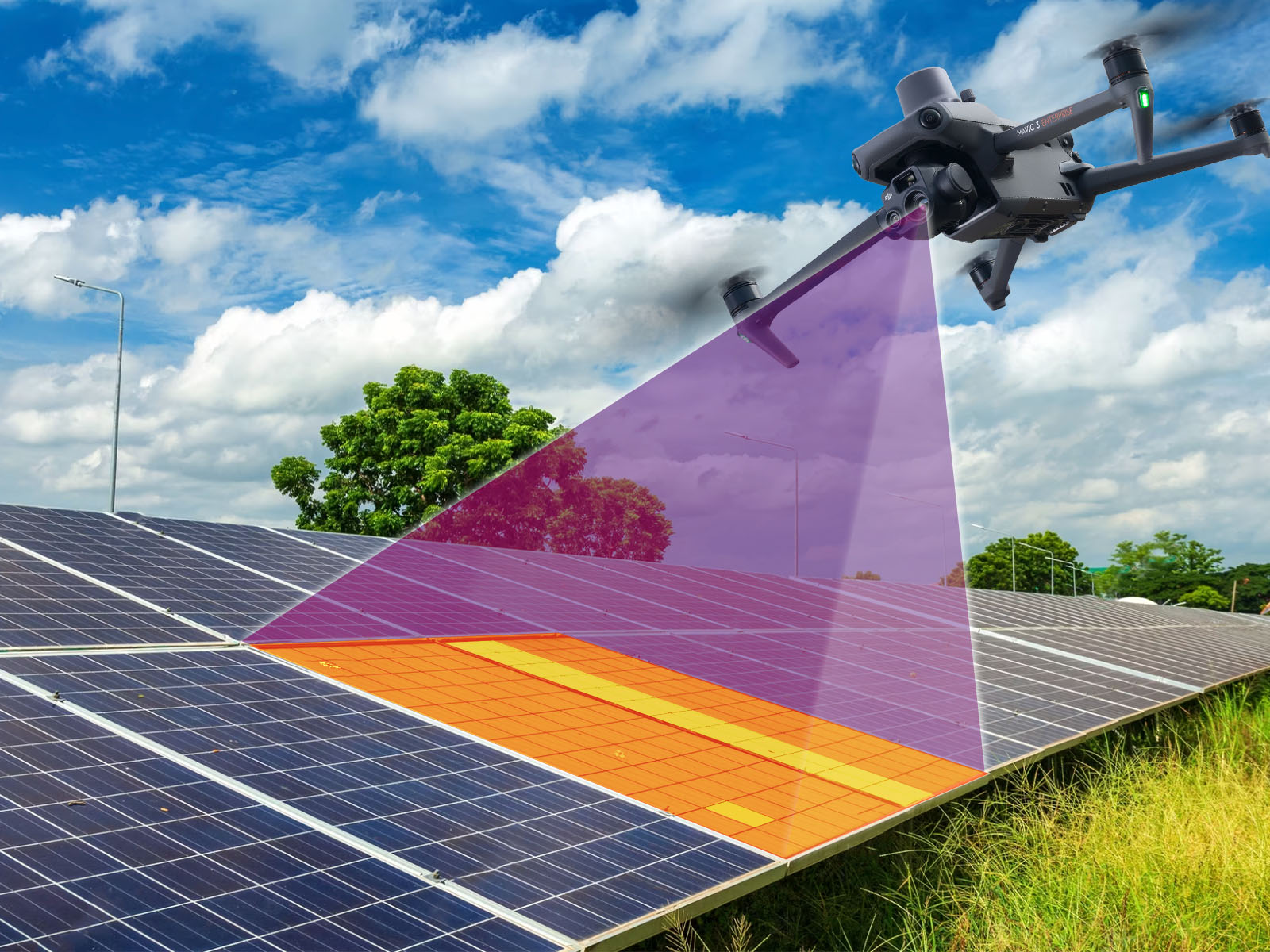
The solar energy industry is growing faster than ever, with solar farms spanning hundreds of acres and generating gigawatts of clean power. But as these projects grow in size and complexity, so does the challenge of maintaining their performance.
That’s where drone technology comes in — transforming how solar farms are inspected, monitored, and maintained. Using drones equipped with thermal cameras, AI analytics, and LiDAR, solar operators can now detect issues early, save costs, and maximize energy output.
The Need for Efficient Solar Farm Monitoring:
A typical utility-scale solar farm can have thousands of panels spread over vast areas. Inspecting them manually is not only time-consuming but also prone to human error.
Manual inspections can take days or even weeks, while drones can cover the same area in a few hours with much higher accuracy.
Efficient monitoring ensures:
• Maximum system uptime
• Faster fault detection
• Reduced maintenance costs
• Higher energy yield
How Drones Revolutionize Solar Inspections:
1. Thermal Imaging for Fault Detection
Drones equipped with infrared (IR) cameras can detect temperature variations across solar modules. These anomalies indicate issues such as:
• Hotspots due to cell damage or dirt buildup
• Faulty bypass diodes
• Connection and junction box failures
• Inverter or string mismatches
Aerial thermography helps technicians pinpoint defective panels before performance drops significantly.
2. Visual and RGB Imaging
High-resolution RGB cameras capture detailed visuals of panels, mounting structures, and wiring. These images are used to identify:
• Physical damage or cracks in panels
• Loose connectors and cables
• Shading from vegetation or debris
Combined with AI-powered image analysis, drones can automatically flag problem areas for maintenance teams.
3. LiDAR and 3D Mapping
Advanced drones use LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) to create precise 3D maps of solar farms.
These maps help in:
• Site planning and layout optimization
• Slope and terrain analysis for water drainage
• Monitoring structural alignment over time
Accurate terrain data ensures optimal solar array design and long-term structural stability.
4. Performance Analytics
Drones integrated with AI and machine learning platforms can process inspection data in real time. They provide actionable insights such as:
• Energy loss estimates due to defects
• Heatmap visualization of inefficiencies
• Predictive maintenance recommendations
This data-driven approach allows operators to schedule maintenance before failures occur — increasing uptime and profitability.
Benefits of Drone-Based Solar Inspection:
| Benefit | Impact |
| Speed | 90% faster inspections compared to manual methods |
| Accuracy | Detects defects at the cell level with thermal precision |
| Cost Savings | Reduces O&M (operations & maintenance) costs by up to 30% |
| Safety | Eliminates human risk in high-voltage or remote areas |
| Data Insights | Provides geotagged, actionable analytics for every panel |
Global Adoption of Drone Technology in Solar:
Countries like the United States, India, China, and Germany are rapidly adopting drone solutions for solar O&M.
• In India, large solar farms in Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Karnataka use drone-based thermal audits to maintain performance in extreme conditions.
• In the US, solar monitoring companies combine drone data with AI-powered asset management platforms to automate reporting and maintenance scheduling.
This trend is expected to accelerate as solar farms expand and data-driven energy management becomes the new standard.
Integration with Other Smart Technologies:
Drones are now part of a larger smart solar ecosystem, integrating with:
• IoT sensors for weather and performance monitoring
• AI-powered analytics dashboards
• Digital twins for real-time virtual inspection
• Autonomous drones that perform scheduled, unmanned inspections
Future of Drone Inspections in the Solar Industry:
The future of solar O&M lies in automation and intelligence. Emerging trends include:
• Swarm drone systems for simultaneous inspection of multiple sites
• AI-based fault classification for automated reporting
• Blockchain-enabled data transparency for asset performance records
• Hybrid drones that can fly longer and operate in challenging terrains
By 2030, drone inspections are expected to become the industry standard, with most large-scale solar farms using autonomous aerial systems.
Conclusion:
Drone technology is redefining how solar farms are maintained. It bridges the gap between efficiency, safety, and sustainability by delivering precise, fast, and actionable insights.
As the solar industry continues to expand globally, drones will play a critical role in optimizing performance, reducing costs, and ensuring that every ray of sunlight is turned into clean, reliable power.
The future of solar monitoring is not just on the ground — it’s in the air.