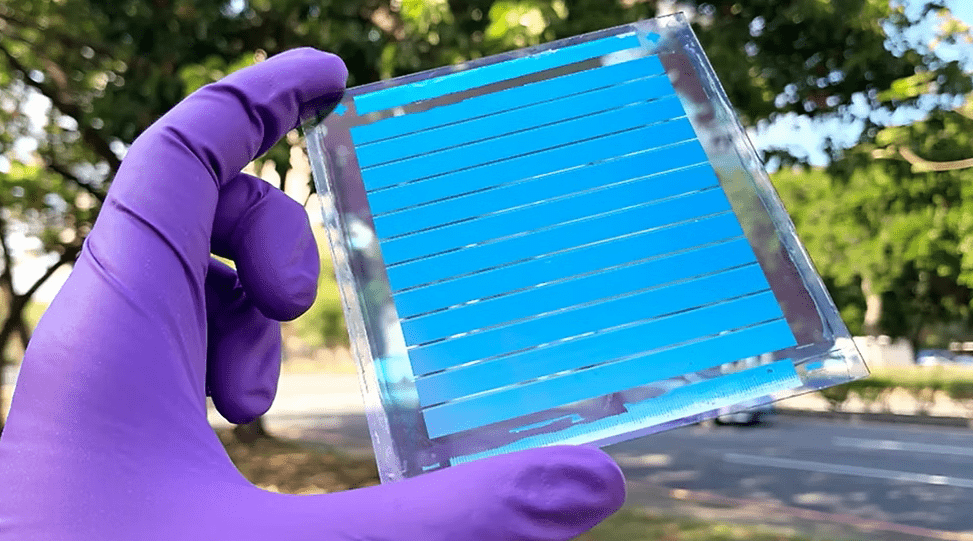
Solar energy is at the heart of the global transition to clean, renewable power. While silicon-based solar panels dominate the market today, researchers and innovators are exploring new materials that could reshape the solar industry. Among these, Organic Solar Cells (OSCs) are emerging as a game-changing photovoltaic (PV) technology, promising lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective solutions.
What Are Organic Solar Cells?
Organic Solar Cells are a type of photovoltaic technology that uses carbon-based (organic) materials instead of traditional silicon to absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity.
● Composition: Made from organic polymers or small molecules.
● Structure: Thin-film layers that can be printed or coated on flexible substrates like plastic or glass.
● Working Principle: Similar to silicon solar cells, they use the photovoltaic effect, but electrons are generated within organic compounds instead of crystalline silicon.
Key Advantages of Organic Solar Cells:
1. Lightweight & Flexible – OSCs can be applied to curved surfaces, fabrics, and even portable devices, opening new possibilities.
2. Low Manufacturing Cost – They can be produced using roll-to-roll printing techniques, making them cheaper and scalable.
3. Semi-Transparent Options – OSCs can be integrated into windows, facades, and greenhouses without blocking natural light.
4. Eco-Friendly Materials – Lower energy and material requirements compared to silicon-based cells.
5. Versatility – They can power wearables, IoT devices, and off-grid applications where traditional panels are impractical.
Challenges Facing Organic Solar Cells:
● Lower Efficiency: Current OSCs typically achieve 15–19% efficiency, compared to 20–25% for silicon.
● Durability Issues: Organic materials degrade faster, reducing lifespan.
● Stability in Harsh Conditions: Sensitive to moisture, oxygen, and UV light, requiring advanced encapsulation.
● Scaling for Mass Production: While cost-effective in theory, commercial adoption still requires significant R&D.
The Current State of Research & Development:
● Researchers are exploring new organic materials with higher absorption and stability.
● Hybrid technologies combining organic and perovskite layers show promise for boosting efficiency.
● Companies and universities are piloting commercial-scale applications for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV).
Applications of Organic Solar Cells:
● Building-Integrated Solar: Semi-transparent windows, skylights, and facades.
● Wearable Electronics: Smart clothing and IoT sensors powered by sunlight.
● Portable Energy Solutions: Lightweight chargers for remote areas and disaster relief.
● Agrivoltaics: Greenhouse-friendly panels that let crops receive light while generating electricity.
The Future Outlook:
Organic solar cells may not immediately replace silicon-based systems, but they complement them by offering flexibility, design freedom, and niche applications. With ongoing research improving efficiency and stability, OSCs could soon become a mainstream option in the renewable energy mix.
Conclusion:
The rise of organic solar cells marks a new era in PV technology. Lightweight, flexible, and versatile, they open doors to applications beyond the scope of traditional solar panels. While challenges remain in efficiency and durability, the future looks bright for OSCs as part of the global effort to make renewable energy more accessible, affordable, and adaptable.